논문 정리
Base 코드와 유사한 논문들을 간단하게 리뷰하려고 합니다.
Contrastive Multiview Coding

인간은 세상을 많은 sensory channels로 봅니다. 각각의 view는 noisy 하고 incomplete 합니다. 하지만 중요한 factor이고 모든 view를 shared하는 경향이 있습니다. 그래서 논문의 저자들은 Multiview contrastive learning이라는 framework 가설을 세우는데 같은 장면의 다른 view사이에 mutual information을 최대화하는 방향으로 represenation을 학습합니다. contrastive loss가 기존의 인기 있었던 cross-view prediction보다 성능이 뛰어나고 view를 더 많이 배울수록 representation 성능이 더 잘나온다는 이러한 approach로부터 나오는 특성을 분석합니다.
Multi-Modality를 사용하는 이유로 서로 다른 information을 종합해서 좀 더 자세히 Classification이 가능하기 때문입니다.
raw-data를 low-dimension인 latenet representation으로 표현 할때 어떤 representation을 좋은 representation이라고 말할 수 있는가? 기본적으로는 AutoEncoder의 Loss가 0이 되거나 GAN 모델들을 사용해서 raw-data를 완벽히 reconstruction 할 수 있는 latent representation을 얻을 수 있는데 이러한 latent representation은 raw-data를 완벽히 압축한 data이기 때문에 필요한 information분만 아니라 noise까지 모두 포함하는 문제가 있다.
논문에서는 이를 Contrastive Loss를 활용해서 Embedding하는 법을 제시한다.

해당 논문에서는 Good bit즉, 좋은 latent representation은 사람이 이해하기 쉽게 Euclidian Distance가 가까우면, 같은 속성을 가지고 있고, 멀리 떨어져있으면 다른 속성을 가지고 있다고 가정하고 있다. 따라서, Multimodality중 같은 Scene은 가깝게 위치하고, 다른 Scene은 멀리 떨어지게 위치하게 하기 위하여 Constrative Loss를 사용하게 된다
해당 논문의 Contribution은 다음과 같습니다.
• We apply contrastive learning to the multiview setting, attempting to maximize mutual information between representations of different views of the same scene (in particular, between different image channels).
• We extend the framework to learn from more than two views, and show that the quality of the learned representation improves as number of views increase. Ours is the first work to explicitly show the benefits of multiple views on representation quality.
• We conduct controlled experiments to measure the effect of mutual information estimates on representation quality. Our experiments show that the relationship between mutual information and views is a subtle one.
• Our representations rival state of the art on popular benchmarks.
• We demonstrate that the contrastive objective is superior to cross-view prediction.
Method
논문의 goal은 인간의 supervision 없이 multiple sensory view 사이의 공유되는 information을 capture하는 represenation을 배우는 것입니다. 이전의 predictive learning method를 언급하고 두 가지 관점(아마 Core View, Full Graph)내에서 contrastive learning에 대해 자세히 얘기하고 mutual information connections 을 maximaization 하는 걸 보여주고 두 view 이상이 포함된 시나리오에 대한 얘기까지 합니다.
Predicitve learning

위 그림을 보면 이해가 편한데 Input(v1)이 Encoder f(.)를 거쳐 latent represenation z로 표현이 됩니다.
이러한 latent representation은 Decoder g(.)을 거쳐 Output(v2햇)로서 나오게 되는데 결과적인 Loss funciton은
v2햇을 v랑 가깝게 해주는 것입니다.
Loss function의 단점으로
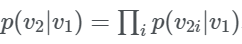
으로서 Complex한 구조와 model correlations의 능력 감소라고 얘기합니다. 이러한 obejective는 v2와 v1의 각 픽셀 또는 요소 사이의 independence를 가정합니다.
Contrastive Learning with Two Views
Integrating Language Guidance into Vision-based Deep Metric Learning(CVPR 2022)
Deep Metric Learning 이기 때문에 사실 상관 없다고 생각하는데...
일반적인 DML 방법은 binary class 할당에 대해 정의된 contrastive ranking 작업을 해결하는 방법을 사용하는데 이러한 접근은 실제 classes의 igher-level semantic 관계를 무시한다고 합니다. 이로 인해 학습된 임베딩 공간이 불완전한 semantic context를 encoding하고 클래스간의 semantic 관계를 잘못 represent해서 학습된 metric 공간의 generalizability 가능성에 영향을 미쳐 좋지 않다고 합니다. visual similarity learning을 위해 language guidance obejective를 제안하는데 language embedding을 expert-and pseudo-classname에 활용함. semantic consistency를 높이기 위해 의미 있는 언어 semantics에 해당하는 visual representation spaces를 문맥화 하고 realing 합니다.
Knowledge Distillation with the Reused Teacher Classifier(CVPR 2022)
Self-Supervised Predictive Learning: A Negative-Free Method for Sound Source Localization in Visual Scenes(CVPR 2022)
Sound sorce localization을 설명하고 (개념) 최근 work들이 contrastive learning framework 에 의존한 localizaiton을 보여주는데 이는 contrastive learning에서 negative sample을 radnom하게 뽀으면 audio와 visual 사이의 misalignment가 일어날 수 있고 그 결과로 localziation의 ambiguity를 야기합니다.
그래서 제안하는 방법이 Self-supervised Predictive Learning입니다. 분명한 positive mining을 통해 sound localization을 위한 negative-free method입니다. 하나의 해당 비디오 프레임의 두 augmented view와 sound source를 associate하기 위해 3개의 stream network를 devise합니다. 이 과정이 audio 와 visual feature간의 semantically로 일관된 similarity로 이어지는겁니다. audio-visual alignment를 위한 새로운 predictive coding module을 소개합니다. 이 모듈이 SSPL이 대상 객체에 점진적으로 focus를 맞출수 있도록 assists하고 positive-pair learning 학습 난이도를 효과적으로 낮춘다.
-> 이 논문은 audio-visual 사이의 정보를 활용해 SOUND LOCALIZAITON task를 함, 컨트리비션이 좋아보임

Contributions
- We propose a novel negative-free method to extend a self-supervised learning framework to the audio-visual data domain for sound localization, and show how it can effectively address the false negative sampling problem
- We propose the predictive coding module for feature alignment, which enables the model to progressively attend to relevant visual features while ignoring information irrelevant to audio cues, boosting sound localization significantly
- Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, which achieves localization performance superior to the state-of-the-art on SoundNet-Flickr and VGG-Sound Source
aduio-visual 은 똑같이 embedding한거 가지고 normalized inner product나 cosine similarity로 두 feature사이의 similarity를 측정하고 이를 활용해 min-max normalization을 진행합니다.
궁금한데 이런 수식으로 진행하는건 어떻게 뭐가 좋고 성능이 잘 나오는지 알고 하는거지....실험적으로 해보는건가...
그 이후에 predictior 하는 건 상관없고 나랑
PCM이라고 predicitive coding MODALITIES 위에서 제안하는 모델이 audio and visual feature alignment를 해준다고 하는데.. 또 이게 localization 퍼포먼스에도 영향을 미친다고 합니다. PC는 feedback connections을 사용하는데 이게 higher-level area부터 lower-level 로 predicitons을 전달하는건데 실제 acitivies랑 predcitions사이의 error를 전달하기 위해 feedforward connections을 사용합니다. dynamicaly하게 업데이트하고요.
이 모델에서는 visual feature를 prior knowledge로 생각하고 반복적인 방식으로 audio feature를 예측합니다.
feedback process는 layer-wise predicition generations 메커니즘으로 representations을 업데이트한다.

식은 다음과 같고 처음에 r0는 original audio feature fa를 의미합니다.
PCM은 prediction error을 줄이기 위해 모든 계층의 representations이 점진적으로 개선되는 동안 두 가지 별도의 프로세스를 교대로 수행합니다. top layer
Self-supervised object detection from audio-visual correspondence(CVPR 2022)
해당 내용이 관련 있으면서 다른 task에서 사용한 방법들이 뭐가 있을까? 그렇게 접근을 해보자..
Object detection이랑 sound source localization이 main task인 논문입니다.
이 논문의 메인은 audio-visual를 이용해 supervision 없이 object detector를 학습하는 문제를 다루는 것입니다. 요새 자주 사용하는 weakly-supervised object detection과 달리 image-level class label을 아예 가정하지 않고 audio-visual data로부터 supervisory signal을 extract해서 사용합니다.


제가 궁금했던 부분은 1번 내용인데 Audio-visual data를 어떻게 활용해서 self-detection을 하는 부분입니다.
두 feature vector의 cosine similarity를 활용해서 spatial locations의 heatmap을 계산하고 이는 sound와 correlated가 있는 물체가 더 강하게 반응할 것이라는 예상을 한다고 합니다. 이 heatmap의 최대값을 가지고 cross entropy loss로 나타내고
두 개의 평균으로 noise-contrastive loss를 나타냅니다.
이 논문은 아이디어는 audio랑 비디오 이미지 같이 사용해서 feature 뽑아서 fusion해서 쓰는건데 이걸로 self-deetection extraction 하는 부분이 컨트리비션입니다. 저랑은 상관이 없을 것 같습니다...
Where and When: Space-Time Attention for Audio-Visual Explanations(arXiv 2021)
dynamic world에서 multiple sensory 모달리티를 모델링 하는건 아직 탐구가 되지 않았다..?
그래서 audio-visual recognition에 대한 학습 가능한 설명을 explore합니다. 이거 뭐지 무슨 task인지 모르겠다.
space-time attention 네트워크를 제안하는데 이건 audio and visual data의 synergistic dynamics을 발견하는 네트워크입니다..
결론적으로는 audio-visual video event를 prediciting하는건데 관련있는 visual cuer가 나타나는 곳을 localizing 하는거랑 비디오에서 sound가 발생하는 곳을 predicted합니다. multi-modal representation learner및 intrinsic explanation 모델과 광범위하게 비교합니다. 관련 task는 audio-visual video event recognition
단순히 두 모달리티를 fusing 하는 대신 각 데이터 양식이 모델 예측에 어떻게 기여하는지 설명하는 동시에 audio-visual video event를 예측할 수 있는 본질적으로 설명 가능한 audio-visual 모델을 제안합니다.
XAI 인것 같음
audio-visual learning의 본질적인 설명 가능성을 달성하기 위해서는 몇가지 challenge가 있는데
(i) the audio and visual information could vary drastically over space and time
(ii) obtaining desired audio-visual recognition and explanation both require learning good representations.